1. Use Another Output Temporarily
Some of the fixes below require that you have a working screen with an available output. Your graphics card likely has other display output types. If your graphics card and TV both have a common port type available other than HDMI, give that a try. This can be a permanent solution (e.g., DisplayPort is a superior option to HDMI) or just a temporary measure until you’ve resolved the problem. If your display only has an HDMI input, you can use an adapter. It’s not particularly expensive to buy a DVI, VGA, or DisplayPort to HDMI adapter these days.
2. Inspect the Cable and Ports for Damage
Before trying anything else, check the HDMI port on your computer and the one on the display for damage such as corrosion or a plug that sits loosely in the port. Check the cable to make sure it isn’t frayed or that the connectors aren’t deformed, corroded, or partially broken from the cable. If you see any kind of damage, replace or repair the components if possible.
3. Try Swapping Out Stuff
To isolate the problem with your HDMI port not working, mix and match components in your connection with other devices to see if the issue is with the display, the computer, or the cable itself. That will help determine which component is at fault.
4. Choose the Right HDMI Port on Your PC
Many desktop computers have integrated graphics available through an HDMI port on the motherboard itself. If you have a discrete GPU installed, make sure to plug the HDMI cable into the card and not into the HDMI port on the motherboard. The picture above is an example of a motherboard connection. A discrete GPU will have the connector on the card itself, accessible through the tall rear slots on the back of the computer. Some computers allow you to run both integrated and discrete cards simultaneously or to switch between them. Those options will be in your BIOS/UEFI menu. Consult your motherboard manual for specific instructions on how to change those settings since they differ from one brand of motherboard to the next.
5. Reboot With the Cable Connected
Try rebooting the computer with the HDMI cable and display connected. While HDMI should work as soon as you plug it in, sometimes Windows may fail to recognize it. Booting with everything in place usually ensures that the display is detected.
6. Select the Correct HDMI Input
Most monitors and televisions have more than one HDMI input. Double-check that you’ve set the display to use the HDMI input you’ve plugged in. You’ll have to check the manual for your screen to see how it’s done, but it’s usually just a setting in the menus.
7. Select the Correct Multi-Monitor Mode in Windows
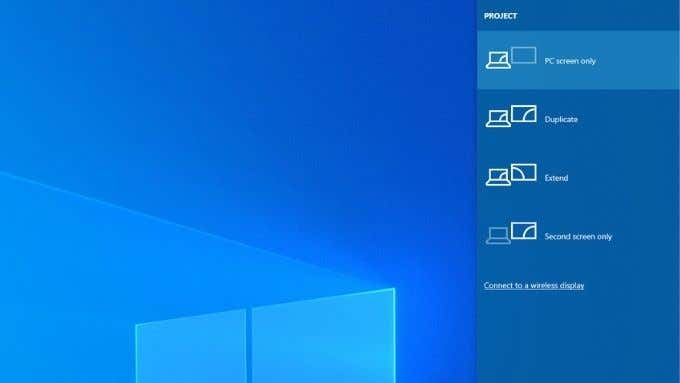
If you’re using the HDMI screen as a second display in a dual-monitor setup, you’ll have to ensure that Windows uses the correct dual monitor mode. You have four options:
Use only one screen.Use only the second screen.Extend the desktop over both screens.Mirror the same desktop to both screens.
To quickly switch between these modes, hold the Windows Key + P. You can then use the mouse pointer to select your preferred mode. If you can’t see anything on any screen, you can hold the Windows Key in and tap P repeatedly to cycle through the different modes.
8. Manually Choose a Supported Resolution and Refresh Rate
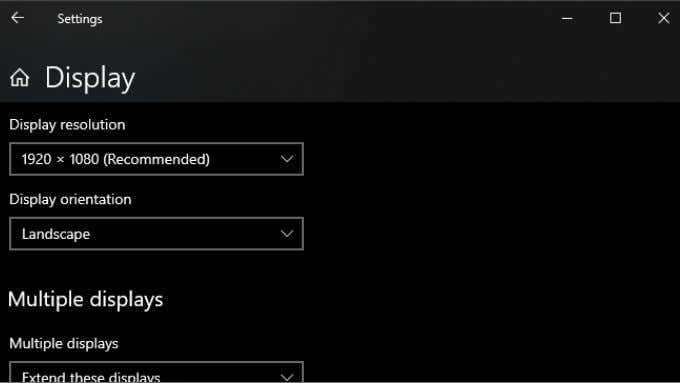
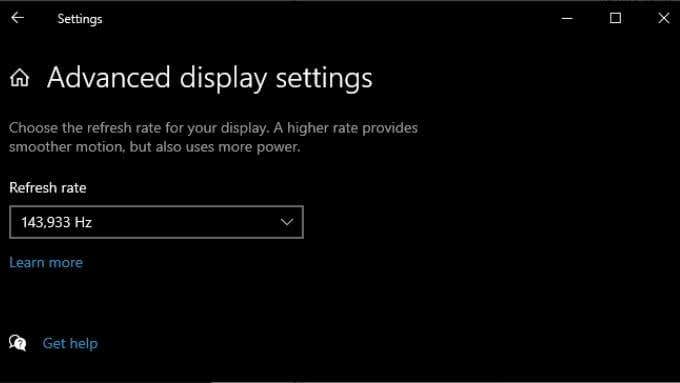
When you connect an HDMI display, your computer should automatically pick the correct resolution and refresh rate. If it fails to do this, the display should show an error message that an unsupported resolution or refresh rate was chosen. In some cases, you won’t see anything or just a “no signal” message. For a secondary display, the easiest fix is to open your display settings and then change the resolution and refresh rate. How you do this depends on the brand of GPU you have since the name of the GPU utility and its layout will differ. What is universal between all brands is that you access these settings by right-clicking on the desktop and then selecting the Nvidia, AMD, or Intel utility from there. Once in the utility, you’ll need to locate the display settings. The example below is for our Nvidia laptop GPU for illustration purposes. You can also use Windows’ own Display Settings page to make these changes: After making these changes and closing the Settings window, your display should be working if this was the problem. Note that HDMI is limited to specific combinations of resolution and refresh rate, depending on the version of HDMI you are using. For example, our screen can achieve 2560×1440 at 165Hz over DisplayPort, but only 144Hz using HDMI.
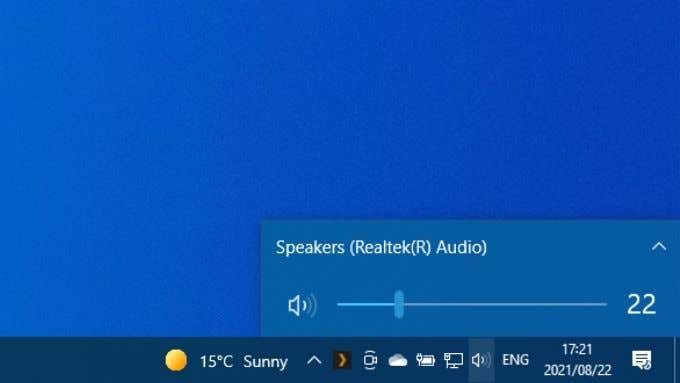
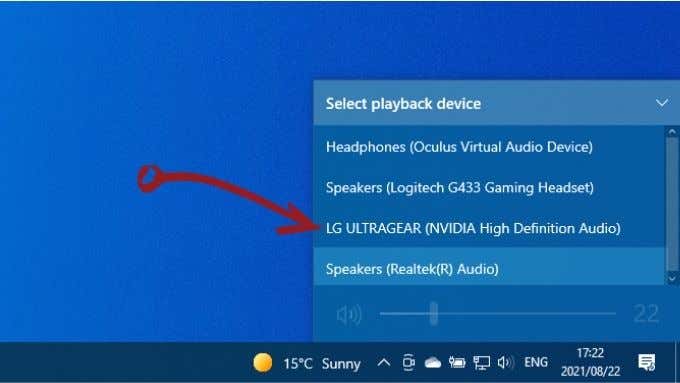
9. Video Works Fine, but There’s No Audio
HDMI carries both video and audio data, and you may find that you have an image but no sound. That’s because Windows 10 treats your HDMI audio stream as a separate sound device. You need to switch to that audio device to use it. Your HDMI device will now be your audio device, and all sound should go to it. If you want to know more about audio routing in Windows 10, read How To Play Sound on Headphones And Speakers At the Same Time In Windows 10.
10. Update Windows and Your GPU Drivers
Finally, make sure that your Windows installation and GPU drivers are both up to date. To make sure you’re running the latest version of Windows 10, open the Start Menu, search for Check for Updates, and then open it. Select the Check for updates button, and Windows will let you know if there are pending updates. As for your GPU drivers, visit the website of your GPU maker and look for your GPU model in the driver download section. In some cases, you can also check for updates using the GPU utility application already installed on your computer. Refer to your GPU’s specific documentation for more detailed instructions.
11. Use the System File Checker
Although it’s a long shot, there is a chance that system file corruption may interfere with your GPU’s operation. The easiest way to make sure all system files are intact is the System File Checker. You can learn how to use the SFC in our SFC and DISM article. It only takes a minute to get going and will usually repair most types of system file corruption.