Just like a desktop publisher, each element in a PowerPoint presentation represents an object that can be positioned without disturbing other objects. These objects include text, images, videos, and any other elements present in your PowerPoint files. Since each object is its own element, you can layer objects to get your presentation to look exactly as you want. Read on to learn why and how to layer objects in a PowerPoint presentation.
Why Layer Objects?
There are two main reasons you may want to layer objects in a PowerPoint presentation. First, layering objects gives you the freedom to arrange your presentation in any layout that you desire. Rather than working in a linear fashion as with a word processor, you can place and layer objects all you want. Second, layering lets you take advantage of all of the white space in your presentation. Text boxes in particular take up a lot of room. By layering objects, you can use all of the space on a slide without changing the position of other objects.
Layering Objects in PowerPoint
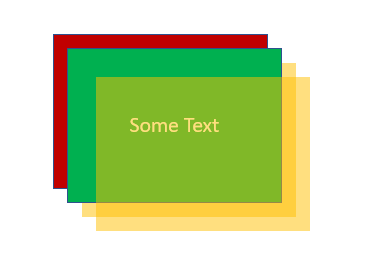
Suppose you add four boxes to your PowerPoint presentation; first a red one, then green, then blue, then yellow. Each box represents an object. When you add a new object to a PowerPoint presentation, the application automatically places the newest objects on top of older objects. If you add the boxes in the order mentioned above, the layering of the objects will look like this:
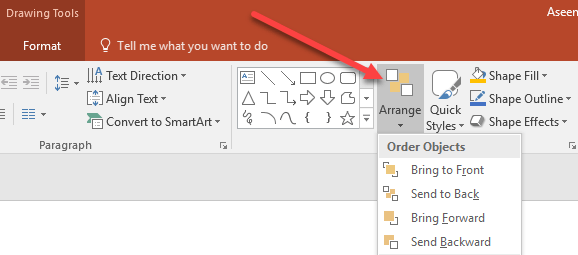
Notice that the newest box (yellow) is on top of the others. Using PowerPoint’s layering function, you can layer these objects in any order. To layer the objects differently from the default order, begin by clicking on the Home tab on the Ribbon and locating the section titled Drawing. In the Drawing section, locate and click on the button titled Arrange.
Notice that on the menu that pops up, there are four options titled: With these commands, you can layer objects in PowerPoint any way you want. Notice, however that the menu items are grayed out; you can’t use them unless you first make an object active by clicking on it before you click on the Arrange button. As an example, let’s arrange the yellow box on top to a different layer. Begin by clicking on the yellow box to make it the active object. Then, click on the Arrange button and select Send Backward from the menu. Notice that now the yellow box has moved back one layer to be between the blue box and the green box.
Now select the blue box and this time select Send to Back from the Arrange menu. Notice that now the blue box occupies the lowest level and is now behind the yellow, green, and red boxes. Using the four arrange functions on the Arrange button, you can choose whether an object moves one level up or down or all the way to the highest or lowest level.
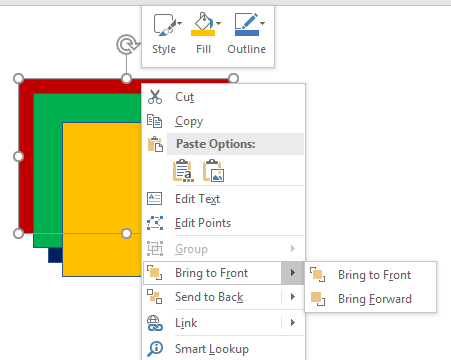
It may take some getting used to working with layers in PowerPoint, but the menu system is quite intuitive. Use the Send Back and Bring Forward commands to move an object one layer back or forward and use the Send to Back and Bring to Forward commands to move an object all the way to the front or back of the layering order. You can also simply right-click on the object and choose those options from the context menu as shown below.
In addition, it’s worth noting that you can also make your layers fully transparent or semi-transparent, which can result in some cool effects. In our little example, I made the yellow layer semi-transparent and then added some text to the green box.
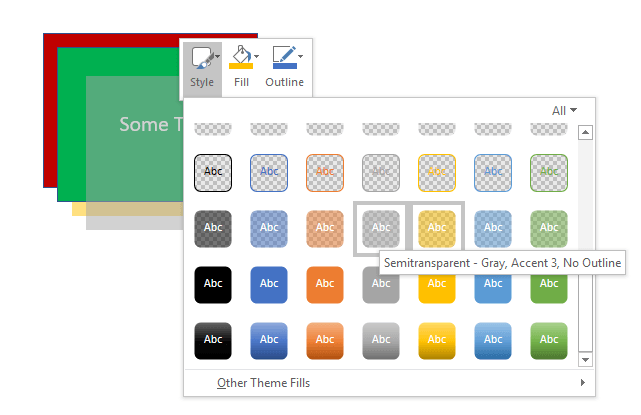
You can make a layer transparent by right-clicking on it and then clicking on the Style button. You’ll see a bunch of boxes with different colors and styles. Towards the middle/bottom, you’ll find the options for transparent and semi-transparent.
There is virtually no limit to the number of layers the objects on a PowerPoint slide can occupy. However, to keep things neat and simple for your audience, consider using no more layers than you need on a single slide. Use too many layers and you risk making too complicated a slide to follow. Experiment with arranging and layering objects in PowerPoint and you can reclaim unused white space to create a more visually appealing PowerPoint presentation. Enjoy!